
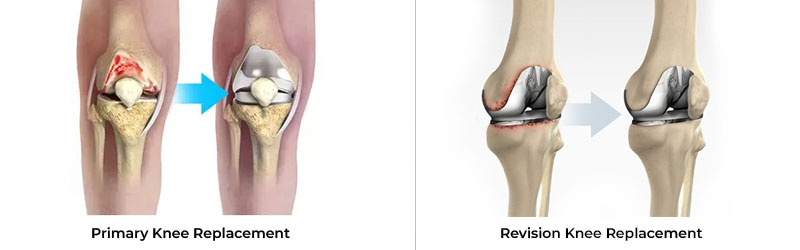
Primary Knee Replacement and Revision Knee Replacement are surgical procedures related to the knee joint, commonly performed to relieve pain and restore function in patients with severe arthritis or knee damage.
Primary knee replacement is the first surgery a patient undergoes to replace a damaged or worn-out knee joint. It is typically performed for conditions like osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, or traumatic injury to the knee joint.
Indications:
Types:
Revision knee replacement is a more complex procedure done when a previously implanted knee prosthesis fails or wears out. It involves removing the old prosthetic components and replacing them with new ones.
Indications:
Both procedures aim to restore function, reduce pain, and improve the patient's quality of life, but revision knee replacement is typically performed after a primary replacement fails or develops complications.